How the Heart Works – Interior View
The Interior of the Heart
Below is a picture of the inside of a normal, healthy, human heart, interior view.
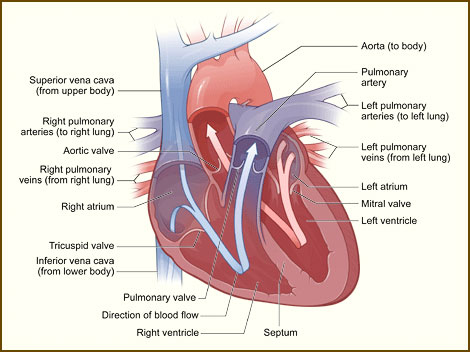
The illustration shows a cross-section of a healthy heart and its inside structures. The blue arrow shows the direction in which low-oxygen blood flows from the body to the lungs. The red arrow shows the direction in which oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs to the rest of the body.
The Septum
The right and left sides of your heart are divided by an internal wall of tissue called the septum. The area of the septum that divides the two upper chambers (atria) of your heart is called the atrial or interatrial septum. The area of the septum that divides the two lower chambers (ventricles) of your heart is called the ventricular or interventricular septum.
Heart Chambers
The picture shows the inside of your heart and how it’s divided into four chambers. The two upper chambers of your heart are called atria. The atria receive and collect blood. The two lower chambers of your heart are called ventricles. The ventricles pump blood out of your heart into the circulatory system to other parts of your body.
Heart Valves
The picture shows your heart’s four valves. Shown counterclockwise in the picture, the valves include the aortic (ay-OR-tik) valve, the tricuspid (tri-CUSS-pid) valve, the pulmonary valve, and the mitral (MI-trul) valve.
Blood Flow
The arrows in the drawing show the direction that blood flows through your heart. The light blue arrows show that blood enters the right atrium of your heart from the superior and inferior vena cavae. From the right atrium, blood is pumped into the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, blood is pumped to your lungs through the pulmonary arteries.
The light red arrows show the oxygen-rich blood coming in from your lungs through the pulmonary veins into your heart’s left atrium. From the left atrium, the blood is pumped into the left ventricle, where it’s pumped to the rest of your body through the aorta.
For the heart to function properly, your blood flows in only one direction. Your heart’s valves make this possible. Both of your heart’s ventricles has an “in” (inlet) valve from the atria and an “out” (outlet) valve leading to your arteries. Healthy valves open and close in very exact coordination with the pumping action of your heart’s atria and ventricles. Each valve has a set of flaps called leaflets or cusps, which seal or open the valves. This allows pumped blood to pass through the chambers and into your arteries without backing up or flowing backward.












